
Introduction
Sodium cyanide (NaCN), as an efficient complexing agent and leaching agent, plays a crucial role in the Metallurgical Industry. Its unique chemical properties enable it to form stable complexes with various metal ions, thus achieving the extraction, separation, and purification of metals. This article will analyze the core applications of Sodium Cyanide in the metallurgical field and summarize the key operation points based on practical experience.
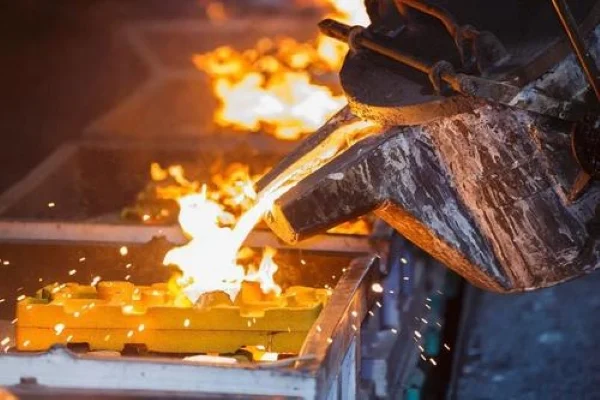

I. Core Uses of Sodium Cyanide in the Metallurgical Industry
1.Gold Extraction (Cyanidation Process for Gold Extraction)
Principle: Sodium cyanide reacts with gold in the presence of oxygen to form soluble gold cyanide complexes (such as [Au(CN)₂]⁻). The gold is then recovered through activated carbon adsorption or zinc displacement.
Advantages: It has strong adaptability to low-grade gold ores and complex ores, and the leaching rate can reach more than 90%.
Case: A gold mine increased the gold recovery rate to 92% by optimizing the concentration of sodium cyanide (0.05%-0.1%) and the leaching time (24-48 hours).
2.Electroplating and Metal Surface Treatment
Purpose: As an additive in Electroplating solutions, it is used for electroplating metals such as copper, zinc, and silver, which can improve the uniformity and adhesion of the coating.
Precautions: The concentration of cyanide needs to be strictly controlled to avoid excessive residue, which may lead to environmental pollution.
3.Metal Separation and Purification
Application Scenarios: Selectively leach the target metals (such as nickel and cobalt) from polymetallic ores, or remove impurity ions (such as iron and lead).
Technical Points: Achieve the stepwise complexation of different metals by adjusting the pH value and the dosage of Sodium cyanide.
II. Key Experience and Technical Optimization in the Use of Sodium Cyanide
1.Control of Concentration and Dosage
Empirical Rule: During gold leaching, the concentration of sodium cyanide is usually 0.03%-0.1%, and it needs to be adjusted according to the properties of the ore (such as carbon content and sulfide content).
Case: A mine found that the consumption of sodium cyanide increased abnormally. After investigation, it was found that the sulfur content in the ore exceeded the standard. The problem was solved after using a pretreatment process (roasting or oxidation).
2.Optimization of Leaching Conditions
pH Value: Maintaining an alkaline environment (pH 10-11) can inhibit the generation of hydrogen cyanide gas and improve the Leaching Efficiency at the same time.
Temperature: Appropriate heating (30-40°C) can accelerate the reaction, but the energy consumption and cost need to be balanced.
3.Environmental Protection and Safety Management
Wastewater Treatment: Use the alkaline chlorination method (sodium hypochlorite + sodium hydroxide) to decompose cyanide to ensure that the discharge meets the standard (the CN⁻ concentration is less than 0.5 mg/L).
Safety Protection: Equip with a fully enclosed production line, an automatic monitoring system, and an emergency sprinkler device. Operators need to wear chemical protective clothing and gas masks.
III. Common Problems and Solutions
1.Risk of Cyanide Poisoning
Preventive Measures: Regularly check the tightness of the equipment and avoid the contact of the cyanide solution with acidic substances (to prevent the generation of highly toxic HCN gas).
Emergency Treatment: Immediately rinse the skin contact area with a large amount of clean water. In case of accidental ingestion, the victim needs to seek medical treatment immediately and be injected with sodium thiosulfate for detoxification.
2.Decrease in Leaching Efficiency
Possible Reasons: Insufficient oxidation degree of the ore, decomposition of sodium cyanide (due to light or high temperature), and interference of impurity ions (such as lead and copper).
Solutions: Add an oxidant (such as hydrogen peroxide) to promote the oxidation of the ore, or remove the impurities through pretreatment.
IV. Future Trends and Alternative Technologies
Cyanide-Free Leaching Technologies: Green processes such as the thiourea method and bioleaching method are gradually emerging, which can reduce environmental risks.
Intelligent Control: Real-time monitoring of parameters such as the concentration of sodium cyanide and pH value through AI algorithms to achieve precise control.
Conclusion
Sodium cyanide has both high efficiency and potential hazards in the metallurgical industry. Rational application depends on scientific process design, strict safety management, and continuous technological innovation. By optimizing operation parameters and strengthening Environmental Protection measures, its value can be maximized and risks minimized, promoting the industry to develop in a green and sustainable direction.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Lead Chloride/ Lead (II) Chloride 98%
- Soda Ash Dense / Light 99.2% Sodium Carbonate Washing Soda
- Flexible Customer and Supplier Relations Specialist (Location: Thailand)
- Shock Tube Detonator
- Potassium borohydride
- Citric acid-Food Grade
- Fertilizer magnesium sulfate/magnesium sulfate monohydrate
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 4International Cyanide(Sodium cyanide) Management Code - Gold Mine Acceptance Standards
- 5China factory Sulfuric Acid 98%
- 6Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 7Soda Ash Dense / Light 99.2% Sodium Carbonate Washing Soda
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Purity · Stable Performance · Higher Recovery — sodium cyanide for modern gold leaching
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4Sodium Hydroxide,Caustic Soda Flakes,Caustic Soda Pearls 96%-99%
- 5Nutritional Supplements Food Addictive Sarcosine 99% min
- 6Sodium Cyanide Import Regulations & Compliance – Ensuring Safe and Compliant Importation in Peru
- 7United Chemical's Research Team Demonstrates Authority Through Data-Driven Insights












Online message consultation
Add comment: