
Sodium cyanide (NaCN), as the core reagent for Gold Extraction, realizes the transformation from ore to gold through the Cyanidation method in Gold Mining. This process involves complex chemical operations and strict process control. The following are the specific usage steps and key technical details:
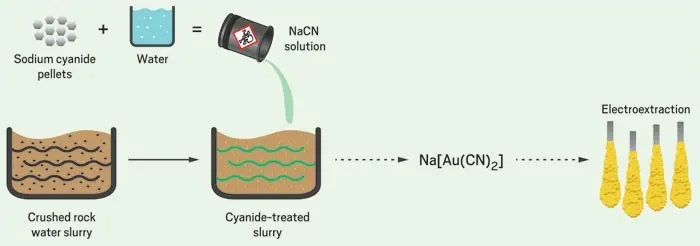
Gold Cyanidation Process
I. Ore Pretreatment
1.Crushing and Grinding
The ore is crushed and ground into fine powder (usually with a particle size ≤ 75μm) to increase the contact area with the Sodium Cyanide solution.
2.Flotation or Gravity Concentration
Low-grade ores need to be pre-concentrated for gold minerals through flotation or gravity concentration to reduce the amount of ore for subsequent cyanidation treatment.
II. Cyanidation Leaching Reaction
1.Leaching Conditions
Solution Preparation: Dissolve sodium cyanide in water to form a dilute solution with a concentration of 0.01%-0.1% (the specific concentration depends on the grade of the ore).
Alkaline Environment: Add calcium oxide (CaO) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to adjust the pH to 10-11 to prevent the decomposition of cyanide into highly toxic hydrogen cyanide (HCN) gas.
Oxygen Supply: Maintain the dissolved oxygen concentration in the solution (usually > 5 mg/L) by aeration or stirring to drive the oxidation reaction.
2.Chemical Reaction
Gold reacts with cyanide in an alkaline and aerobic environment to form soluble complexes:
4Au + 8NaCN + O₂ + 2H₂O → 4NaAu(CN)₂ (sodium aurocyanide) + 4NaOH
This reaction needs to last for several hours to several days to ensure that the gold is fully dissolved.
III. Precipitation and Recovery of Gold
1.Zinc Replacement Method
Add zinc powder or zinc wire to the leaching solution, and gold is precipitated through a replacement reaction:
2Au(CN)₂⁻ + Zn → 2Au↓ + Zn(CN)₄²⁻
The generated gold powder is washed and smelted to obtain crude gold.
2.Activated Carbon Adsorption Method
In an alternative solution, activated carbon can selectively adsorb Au(CN)₂⁻ in the solution, and then the gold is recovered through high-temperature desorption.
IV. Tailings Treatment and Safety Control
1.Neutralization of Cyanide
The tailings pulp after leaching needs to oxidize the residual cyanide by adding sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) or hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂):
CN⁻ + ClO⁻ + H₂O → CNO⁻ + Cl⁻ + 2OH⁻
Finally, reduce the cyanide concentration to the environmental safety standard (usually < 0.5 mg/L).
2.Closed-loop Circulation System
Adopt a closed process to reduce the discharge of the cyanide solution, and the reuse rate of some enterprises can reach more than 90%.
V. Technical Difficulties and Optimization Directions
1.Interference of Impurities
Metal ions such as copper and iron will consume cyanide. Pretreatment (such as roasting for desulfurization) or the addition of inhibitors (such as sodium sulfide) is required to reduce the impact.
2.Treatment of Low-grade Ores
For finely disseminated and enclosed gold, biological pre-oxidation (such as bacterial leaching) or pressure oxidation technology is adopted to break the mineral structure and improve the gold leaching rate.
3.Upgrading of Environmental Protection Technologies
Develop low-cyanide or cyanide-free leaching agents (such as thiosulfates), and explore new recovery processes such as electrochemical deposition.
Conclusion
The application of Sodium cyanide in gold mining depends on precise process control and strict safety management. Although its toxicity has caused controversy, its high efficiency and economic benefits still make it the mainstream technology. In the future, with the improvement of environmental protection requirements, the cyanidation method will develop in coordination with green technologies, promoting the transformation of gold mining towards a safer and more sustainable direction.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Ferrous Sulfate Industrial Grade 90%
- Sodium Persulfate,Sodium Persulphate,supplier 99.00%
- Potassium borohydride
- Dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid
- Pharmaceutical Intermediate Glycine with High Quality 99%
- 99.5% Pure Ethylene Glycol Mono Ethylene Glycol MEG EG
- Sodium nitrate
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 4International Cyanide(Sodium cyanide) Management Code - Gold Mine Acceptance Standards
- 5China factory Sulfuric Acid 98%
- 6Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 7Soda Ash Dense / Light 99.2% Sodium Carbonate Washing Soda
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Purity · Stable Performance · Higher Recovery — sodium cyanide for modern gold leaching
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4Sodium Hydroxide,Caustic Soda Flakes,Caustic Soda Pearls 96%-99%
- 5Nutritional Supplements Food Addictive Sarcosine 99% min
- 6Sodium Cyanide Import Regulations & Compliance – Ensuring Safe and Compliant Importation in Peru
- 7United Chemical's Research Team Demonstrates Authority Through Data-Driven Insights












Online message consultation
Add comment: