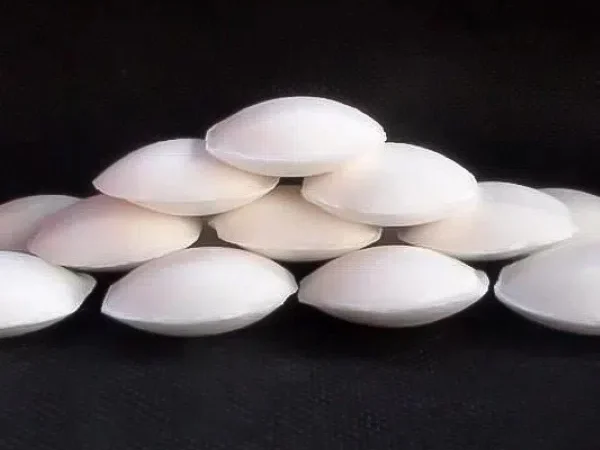

Sodium cyanide (NaCN), as a highly toxic yet efficient chemical raw material, plays an irreplaceable role in the industrial field due to its unique chemical properties. Its applications cover multiple key industries, ranging from the Extraction of Precious Metals to fine chemical synthesis. However, with the tightening of environmental protection regulations and the rise of green technologies, the future development of Sodium Cyanide is facing new challenges and opportunities.

I. Core Application Areas of Sodium Cyanide
1. Extraction of Precious Metals and Mineral Processing
Sodium cyanide is a core reagent in the mining of gold and silver. Through the cyanidation method, it can form soluble complexes with gold and silver, enabling the efficient extraction of precious metals from low-grade ores. The reaction equation is as follows:
4Au + 8NaCN + O₂ + 2H₂O → 4NaAu(CN)₂ + 4NaOH
Despite the risk of toxicity, the cyanidation method still accounts for more than 80% of the global gold extraction volume due to its low cost and high recovery rate.
2. Electroplating and Surface Treatment
In the electroplating industry, sodium cyanide, as a complexing agent, can stabilize metal ions (such as copper, zinc, and cadmium) to ensure a uniform and dense plating layer. For example, the cyanide zinc plating process can significantly improve the corrosion resistance of steel. However, due to environmental protection pressures, cyanide-free electroplating technologies (such as zincate zinc plating) are gradually replacing traditional processes.
3. Organic Synthesis and Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Sodium cyanide is an important raw material for the synthesis of nitrile compounds. Through nucleophilic substitution reactions, the CN⁻ group can be introduced into organic molecules to produce key intermediates such as acrylonitrile (for synthetic fibers) and adiponitrile (for nylon 66). For example:
CH₂=CHCH₂Cl + NaCN → CH₂=CHCH₂CN + NaCl
In the pharmaceutical field, Sodium cyanide is involved in the synthesis of vitamin B12. anti-cancer drugs, and so on.
4. Pesticides and Insecticides
Sodium cyanide can be used to prepare a variety of insecticides, such as fenvalerate (a pyrethroid insecticide). Its derivative, thiocyanate (SCN⁻), is also used in herbicides and fungicides.
5. Other Industrial Applications
Metal Cleaning: Removing the oxide layer on the metal surface;
Mineral Processing Inhibitor: Adjusting the flotation behavior of minerals;
Precursor of Chemical Weapons: A sensitive application that requires strict control.
II. Development Prospects: Challenges and Opportunities Coexist
1. Environmental Protection and Safety Pressures
The high toxicity of sodium cyanide has compelled the world to strengthen supervision. For example, the EU's Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) Regulation lists it as a substance of very high concern (SVHC), requiring enterprises to disclose usage information. Leakage accidents may lead to ecological disasters (such as the Tianjin Port explosion incident in China in 2015), driving the industry to transform towards the goal of "zero emissions".
2. Technological Innovation and Alternative Solutions
Popularization of Cyanide-free Processes:
Gold Extraction: Technologies such as thiourea leaching and bromination method are gradually maturing;
Electroplating: Using complexing agents like citrates and ethylenediamine to replace cyanides;
Green Synthesis Pathways: Synthesizing nitrile compounds through biocatalysis methods (such as using nitrile hydratase to produce acrylamide);
Circular Economy Model: Developing cyanide recovery technologies (such as membrane separation and ion exchange) to reduce consumption.
3. Growth Potential in High-value-added Fields
New Energy Materials: Sodium cyanide is used in the synthesis of precursors for cathode materials of lithium-ion batteries (such as lithium nickel cobalt manganate);
Electronic Chemicals: Used as an etchant in the manufacturing of semiconductor wafers;
Pharmaceutical Intermediates: With the acceleration of innovative drug research and development, the demand for sodium cyanide in fine chemicals may continue to grow.
4. Regional Market Differentiation
Developed Countries: The demand tends to be stable, with the focus shifting to technological upgrading and environmental compliance;
Emerging Markets: The expansion of infrastructure and manufacturing industries drives the demand, such as the gold mining development in Southeast Asia and Africa.
III. Future Trends and Industry Responses
1.Technological Upgrades: Developing processes with low concentrations of sodium cyanide and optimizing reaction conditions to reduce usage;
2.Digital Management: Real-time monitoring of the use of sodium cyanide through the Internet of Things (IoT) to enhance safety;
3.Policy Guidance: The government needs to balance industrial demand and environmental protection goals and promote "Responsible Cyanide Management" (such as the International Cyanide Management Code, ICMI);
4.Public Communication: Strengthening industry transparency and reducing social cognitive biases towards cyanide.
Conclusion
The industrial value of sodium cyanide coexists with its toxicity risks. In the future, its development will rely on the synergistic effect of technological innovation and strict supervision. Although it faces substitution pressures in some fields, its irreplaceability in high-value-added industries, as well as breakthroughs in green processes, may still open up new growth spaces for it. Just like other hazardous substances in the chemical industry, the path to the sustainable development of sodium cyanide lies in "controlling risks and releasing value".
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- T-610 collector Salicyl oxime acid derivative Content 3.5%
- Powdery emulsion explosive
- Calcium Peroxide 60% Assay Yellowish Tablet
- Ferrous Sulfate Industrial Grade 90%
- Potassium Permanganate – Industrial Grade
- Sodiumsulfite Technical Grade 96%-98%
- Food Grade Heavy Light Precipitated Calcium Carbonate Powder Granular 99%
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 4International Cyanide(Sodium cyanide) Management Code - Gold Mine Acceptance Standards
- 5China factory Sulfuric Acid 98%
- 6Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 7Oxalic acid for mining 99.6%
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Quality 99% Purity of Cyanuric chloride ISO 9001:2005 REACH Verified Producer
- 3Zinc chloride ZnCl2 for High Molecular Weight Polymers Initiator
- 4High Purity · Stable Performance · Higher Recovery — sodium cyanide for modern gold leaching
- 5High Quality Sodium Ferrocyanide / Sodium Hexacyanoferr
- 6Gold Ore Dressing Agent Safe Gold Extracting Agent Replace Sodium Cyanide
- 7Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9










Online message consultation
Add comment: