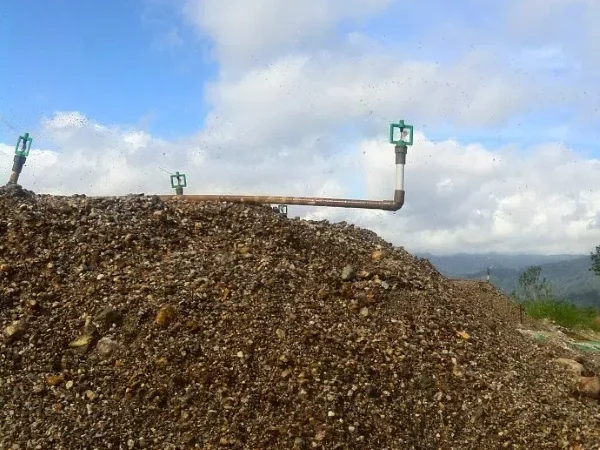

Gold extraction through crushing and heap leaching is a widely adopted method in the gold mining industry. To ensure efficient and sustainable gold recovery, operators need to pay close attention to multiple aspects throughout the process.
1. Analysis of Ore Properties
Mineral Composition
Understanding the gold content and associated minerals in the ore is crucial. This step helps determine whether the heap leaching method is applicable. For instance, if the ore contains a large amount of refractory minerals, additional pretreatment may be required.
Particle Size Distribution
After crushing, the particle size of the ore must be uniform. Oversized particles can lead to incomplete leaching, while undersized particles may generate excessive fines, impeding solution penetration.
2. Crushing Process
Crushing Equipment
Select appropriate crushers, such as jaw crushers and cone crushers. These machines are designed to break down the ore to the required particle size. For example, jaw crushers are effective for primary crushing, while cone crushers are suitable for secondary and tertiary crushing.
Particle Size Control
Typically, the particle size should be controlled between 10 - 30 millimeters. Oversized particles reduce the leaching rate, and undersized particles can cause issues with solution percolation due to the formation of fines.
3. Preparation of Heap Leaching Sites
Site Selection
Choose a flat and impervious area for heap leaching. This helps prevent solution leakage, which could contaminate the environment.
Impermeability Treatment
Lay an impermeable membrane to prevent leachate from seeping into the ground. This is essential for environmental protection and efficient leaching.
4. Selection and Use of Leaching Agents
Leaching Agents
Sodium cyanide solution is commonly used as a leaching agent. The concentration of Sodium cyanide should be strictly controlled within 0.05% - 0.1%. A higher concentration increases costs, while a lower concentration reduces the leaching rate.
pH Value Control
Maintain the pH value of the leaching solution between 10 - 11. This helps prevent the decomposition of cyanide, ensuring the effectiveness of the leaching process.
5. Heap Leaching Operations
Heap Height Control
The heap height is usually set between 3 - 6 meters. An overly high heap can impede solution penetration, while an overly low heap reduces production efficiency.
Spraying Intensity
Control the spraying intensity at 5 - 10 L/m²·h. Excessive spraying leads to solution loss, while insufficient spraying affects the leaching effect.
6. Management of Leachate
Leachate Collection
Ensure effective collection of leachate to avoid loss and environmental pollution. A well - designed collection system is essential for maximizing gold recovery.
Leachate Recycling
Recycle the leachate to improve gold recovery and reduce reagent consumption. This not only increases efficiency but also reduces costs.
7. Environmental Protection
Wastewater Treatment
Treat the leachate before discharging it to prevent environmental pollution. This may involve processes such as chemical precipitation and filtration.
Tailings Disposal
Properly dispose of the tailings after leaching to prevent secondary pollution. Options include safe storage in tailings ponds or further processing.
8. Safety Management
Cyanide Management
Cyanide is highly toxic. Implement strict management measures to prevent leakage and poisoning. This includes proper storage, handling, and transportation of cyanide.
Personnel Protection
Operators should wear appropriate protective equipment. Regular training is also necessary to ensure safe operation.
9. Equipment Maintenance
Regular Inspection
Regularly inspect crushing, spraying, and other equipment to ensure normal operation. This helps identify potential problems before they cause significant disruptions.
Timely Repair
Repair any faults promptly to avoid production delays. A well - maintained equipment fleet is essential for continuous and efficient production.
10. Cost Control
Reagent Cost
Optimize the use of reagents to reduce costs. This may involve adjusting reagent concentrations based on ore properties and leaching results.
Energy Consumption Control
Optimize the crushing and spraying processes to reduce energy consumption. This not only cuts costs but also contributes to environmental sustainability.
In conclusion, gold extraction through crushing and heap leaching requires comprehensive consideration of ore properties, process parameters, environmental protection, and safety management. By paying attention to these key points, operators can improve gold recovery rates and achieve sustainable development in the gold mining industry.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Magneto Electric Detonator(Anti stray current)
- Anhydrous Ammonia 99% Liquid
- United Chemical GDA Gold Dressing Agent HS: 3824999999 – Eco-Friendly Substitute for Sodium Cyanide
- Diethylene Glycol
- Adipic acid 99% used as the material of nylon 66
- Sodium alpha olefin sulfonate (AOS)
- 99% Animal Feed Additive DL Methionine
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 4International Cyanide(Sodium cyanide) Management Code - Gold Mine Acceptance Standards
- 5China factory Sulfuric Acid 98%
- 6Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 7Soda Ash Dense / Light 99.2% Sodium Carbonate Washing Soda
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Purity · Stable Performance · Higher Recovery — sodium cyanide for modern gold leaching
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4Sodium Hydroxide,Caustic Soda Flakes,Caustic Soda Pearls 96%-99%
- 5Nutritional Supplements Food Addictive Sarcosine 99% min
- 6Sodium Cyanide Import Regulations & Compliance – Ensuring Safe and Compliant Importation in Peru
- 7United Chemical's Research Team Demonstrates Authority Through Data-Driven Insights












Online message consultation
Add comment: