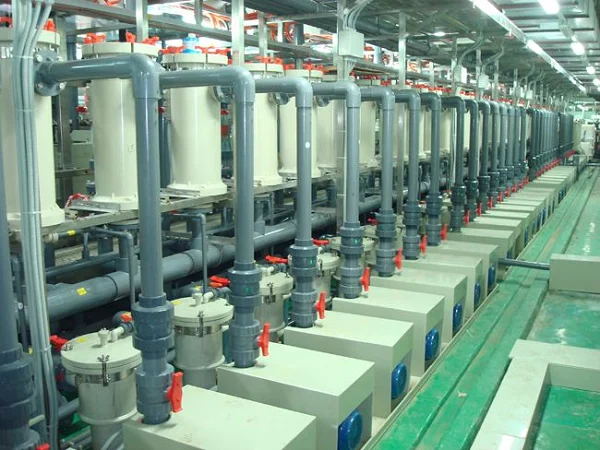

Sodium Cyanide (NaCN) is a widely used chemical reagent in Organic Synthesis. It plays a pivotal role in diverse reactions, and its applications span multiple fields, from pharmaceutical Synthesis to the dye industry. This article delves into the various uses and mechanisms of Sodium Cyanide in organic synthesis.

1. Roles as a Nucleophile and a Base
Sodium cyanide is frequently employed as a Nucleophile. It can undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions with halogens in many organic compounds, such as alkyl halides and aryl halides, thereby introducing the cyanide ion. This type of reaction typically requires basic conditions, and sodium cyanide serves a dual purpose here, acting as both a nucleophile and a Base.
2. A Key Intermediate in Amino Acid Synthesis
Sodium cyanide also plays a crucial role in the synthesis of Amino Acids. Through reactions in the presence of sodium cyanide, alkyl halides, and ammonia, important intermediates for amino acids can be prepared. This intermediate can then be used to synthesize polypeptides, proteins, and other biomolecules.
3. Environmental Impact of Sodium Cyanide in Compound Synthesis
Despite its significant applications in organic synthesis, sodium cyanide raises concerns regarding environment and safety. It is a highly toxic substance and requires careful handling during synthesis. Moreover, proper disposal of waste sodium cyanide is essential to prevent environmental pollution.
4. Applications of Sodium Cyanide in Metal Extraction
Furthermore, sodium cyanide plays an important role in metal smelting and extraction. For instance, it is commonly used to extract gold and silver, forming the corresponding cyanides, which can then be recovered through reduction or other methods.
5. Reactions in Biochemistry
In Biochemistry, sodium cyanide is also used in certain experiments and reactions. For example, it can be used to inhibit cell respiration, which is of great significance in some research areas.
In conclusion, sodium cyanide plays multiple important roles in organic synthesis, from nucleophilic substitution reactions to amino acid synthesis, each with its unique mechanisms and applications. However, extreme caution is required when using sodium cyanide due to its toxicity, and due consideration should be given to its environmental and safety aspects. Understanding the chemical properties and reaction mechanisms of sodium cyanide is crucial for its effective and safe application in organic synthesis.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMCERTIFICATE
- 31%-36% HCl/Industrial Grade Hydrochloric Acid
- Flexible Customer and Supplier Relations Specialist (Location: India)
- High-strength, High-precision Shock Tube Detonator
- Calcium Peroxide 60% Assay Yellowish Tablet
- calcium chloride anhydrous for food
- Food Grade Ammonium Sulphate
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 4International Cyanide(Sodium cyanide) Management Code - Gold Mine Acceptance Standards
- 5China factory Sulfuric Acid 98%
- 6Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 7Oxalic acid for mining 99.6%
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Quality 99% Purity of Cyanuric chloride ISO 9001:2005 REACH Verified Producer
- 3Zinc chloride ZnCl2 for High Molecular Weight Polymers Initiator
- 4High Purity · Stable Performance · Higher Recovery — sodium cyanide for modern gold leaching
- 5High Quality Sodium Ferrocyanide / Sodium Hexacyanoferr
- 6Gold Ore Dressing Agent Safe Gold Extracting Agent Replace Sodium Cyanide
- 7Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9










Online message consultation
Add comment: