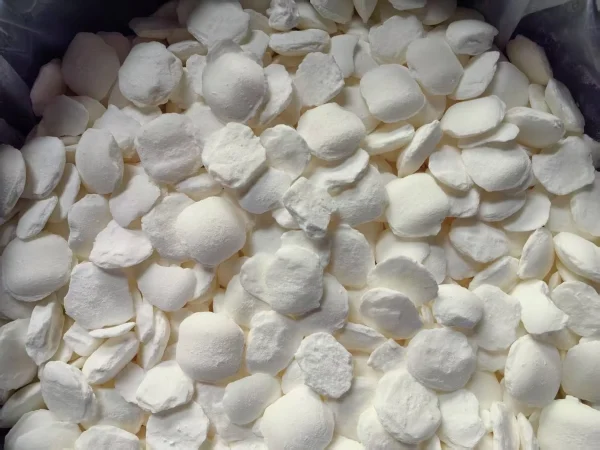

Cyanide, a chemical compound containing the cyano group with a carbon atom triple - bonded to a nitrogen atom, is well - known for its high toxicity. However, it also plays several important roles across various industries due to its unique chemical properties.
1. Mining Industry
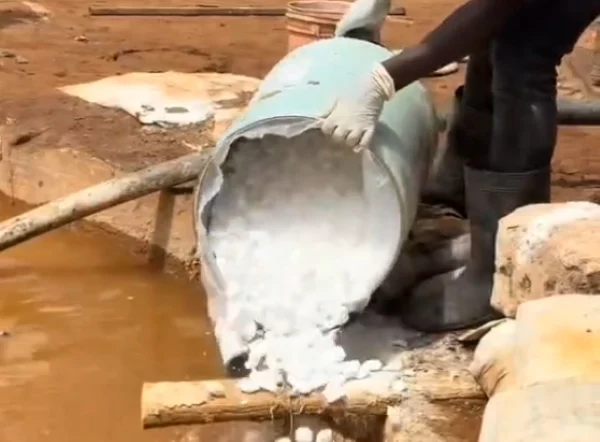
One of the most significant applications of Cyanide is in the Mining industry, especially in the extraction of precious metals like gold and silver. The process is called cyanidation or the cyanide process.
Gold
and ilver ExtractionS
Ore Processing: Cyanide solutions are used to dissolve gold and silver from the mined ore. Gold, in its native form, has a relatively high oxidation potential. But when in the presence of cyanide ions (\(CN^-\)), the gold forms a soluble complex ion. This chemical interaction enables the gold to dissolve in the cyanide solution, separating it from the other components of the ore.
Similarly for silver, it reacts with cyanide in a comparable manner to form a soluble complex, allowing it to be extracted from the ore matrix.
After the precious metals are dissolved in the cyanide solution, they can be recovered through electrochemical methods such as electrowinning. In electrowinning, an electric current is passed through the solution, causing the metal ions to be deposited onto a cathode. Another method is precipitation, for example, by adding a more reactive metal like zinc. The zinc displaces the gold or silver from the complex ion in the solution, enabling the recovery of the precious metals.
2. Chemical Manufacturing
Cyanide compounds are crucial intermediates in the production of a wide range of chemicals.
Plastics
Cyanide derivatives are used in the production of synthetic rubber and plastics. For instance, acrylonitrile, which contains a cyano group, is a key monomer in the production of polyacrylonitrile (PAN). PAN is used to make acrylic fibers, which are used in the textile industry for making clothing, carpets, and upholstery. Through a polymerization process, acrylonitrile molecules link together to form long chains of polyacrylonitrile.
Dyes
Certain textile dyes are synthesized using cyanide - based chemicals. Cyanide - containing compounds can be used to introduce functional groups into dye molecules, which can affect their color, solubility, and fastness properties. For example, some reactive dyes that can form covalent bonds with textile fibers during dyeing may contain cyanide - derived functional groups, contributing to the dye's ability to adhere to and color the fabric effectively.
Pharmaceuticals
Cyanide plays a role in the manufacturing of drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Although the use of cyanide in pharmaceuticals is highly regulated due to its toxicity, it can be involved in chemical reactions during the synthesis of complex organic molecules. For example, in some multi - step synthetic routes for drugs, cyanide may be used to introduce a cyano group into the molecule. This cyano group can then be further modified through processes like hydrolysis to form carboxylic acids, or reduction to form amines, which are important functional groups in many drugs.
3. Electroplating and Metal Treatment
Cyanide solutions are widely employed in electroplating processes.
Jewelry Manufacturing
In the production of high - quality jewelry, cyanide - based electroplating solutions are used to deposit metals such as gold, silver, and copper onto surfaces. Cyanide acts as a complexing agent, which helps in achieving a smooth, uniform, and adherent metal coating. For example, in gold electroplating, the gold - cyanide complex in the solution allows for better control of the deposition rate and the quality of the gold layer on the jewelry substrate. During electroplating, the gold - cyanide complex dissociates at the cathode, and the gold ions are reduced to form a thin, even layer of gold on the surface of the jewelry.
Electronics
In the electronics industry, cyanide - based electroplating is used to coat components. This improves the conductivity and corrosion resistance of electronic parts. For example, copper - cyanide electroplating is used to deposit a thin layer of copper on printed circuit boards (PCBs). The copper layer provides good electrical conductivity, and the use of cyanide in the electroplating bath helps in obtaining a uniform and defect - free copper coating, which is essential for the proper functioning of the PCB.
4. Other Industrial Applications
Metal Quenching
Cyanide compounds can be used in the heat treatment of metals, specifically in a process called cyaniding. In cyaniding, steel parts are heated in a bath containing a cyanide salt. This process introduces carbon and nitrogen into the surface of the steel, hardening it. As the cyanide decomposes at high temperatures, the carbon and nitrogen atoms diffuse into the steel surface, forming hard compounds such as iron nitrides and carbides. These compounds enhance the wear and fatigue resistance of the metal, making it more durable for various applications.
Organic Synthesis
Cyanide is used to introduce a cyano group (\(-CN\)) into organic molecules, forming organic cyanides (nitriles). These nitriles can be further transformed into other functional groups. For example, hydrolysis of a nitrile in the presence of an acid or a base can yield a carboxylic acid. Reduction of a nitrile can lead to the formation of an amine. This makes cyanide a valuable building block in the synthesis of a wide variety of organic compounds, including those used in the production of perfumes, flavors, and other specialty chemicals.
Production of Other Chemicals
Cyanide is used in the production of chemicals such as cyanuric chloride. Cyanuric chloride is an important intermediate in the production of herbicides, pesticides, and dyes. It is produced by the trimerization of cyanogen chloride, which is often synthesized from cyanide sources. Through this chemical transformation, cyanide contributes to the creation of compounds that are essential for various industries, from agriculture to textile dyeing.
In conclusion, despite its highly toxic nature, cyanide's unique chemical reactivity makes it an essential compound in multiple industrial processes. However, due to its extreme toxicity, strict safety measures and environmental regulations are in place to ensure its proper handling, use, and disposal in industrial settings.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Sulphuric Acid 98% Industrial Grade
- industry Electric Detonator
- 99.5% min Ammonium Chloride For Industrial Use
- Food Grade Heavy Light Precipitated Calcium Carbonate Powder Granular 99%
- Dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- lithium Carbonates 99.5% Battery Level or 99.2% Industry grade 99%
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 3China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 4International Cyanide(Sodium cyanide) Management Code - Gold Mine Acceptance Standards
- 5China factory Sulfuric Acid 98%
- 6Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 7Soda Ash Dense / Light 99.2% Sodium Carbonate Washing Soda
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Purity · Stable Performance · Higher Recovery — sodium cyanide for modern gold leaching
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9
- 4Sodium Hydroxide,Caustic Soda Flakes,Caustic Soda Pearls 96%-99%
- 5Nutritional Supplements Food Addictive Sarcosine 99% min
- 6Sodium Cyanide Import Regulations & Compliance – Ensuring Safe and Compliant Importation in Peru
- 7United Chemical's Research Team Demonstrates Authority Through Data-Driven Insights












Online message consultation
Add comment: