
The Prevalence and Drawbacks of Cyanidation Process
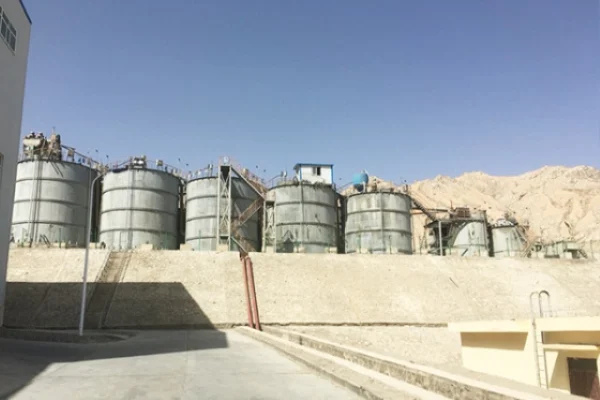
The Cyanidation process occupies a dominant position in global gold extraction and metallurgy. It is widely lauded for multiple advantages. Its high recovery rate ensures maximum gold extraction. The process’s adaptability to various ore types makes it versatile. Operationally, it is simple, and cost - effective, which is a huge plus for mining companies. Additionally, it prevents losses during gold ore transportation. However, a significant drawback of this process is the generation of a substantial amount of Cyanide tailings.
Environmental and Safety Hazards Posed by Cyanide Tailings
The disposal of cyanide tailings presents severe environmental and safety challenges. These tailings occupy vast tracts of land, leading to a waste of precious land resources. More importantly, they waste valuable mineral resources that could otherwise be utilized. The residual toxins in cyanide tailings can contaminate rivers and soil, severely disrupting the ecological balance. On top of that, tailings dams associated with cyanide tailings pose potential safety hazards. Dam failures can trigger catastrophic consequences, endangering lives and property.
Current Approaches and Their Limitations
Despite being classified as waste, cyanide tailings have great potential for resource recovery. Currently, a common practice is to enrich sulfur in cyanide tailings and use it as a raw material for sulfuric acid production. Subsequently, the resulting slag is directly used as iron powder. However, this approach has two major limitations. First, the iron powder contains gold. This reduces the overall Resource utilization rate and economic returns. Second, the iron grade of the slag is relatively low. Given that the iron grade is directly proportional to the metallurgical value, improving the iron grade can notably enhance the efficiency of smelting.
The Significance of High - Value Utilization of Cyanide Tailings
Developing a high - value utilization method for sulfur, iron, and gold in cyanide tailings is of utmost significance. This innovative approach aims to maximize the economic value of cyanide tailings. By doing so, it effectively addresses both environmental and economic challenges. It represents a crucial step towards sustainable development in the mining industry, offering a win - win solution for resource conservation and economic growth.
- Random Content
- Hot content
- Hot review content
- Sodium Isopropyl Xanthate 90% SIPX
- Oxalic acid for mining 99.6%
- Booster(Detonating insensitive explosives)
- Sodium Metal, ≥99.7%
- Lithium hydroxide 99% Solid
- Diethylene Glycol
- Ethyl alcohol /Ethanol 99.5%
- 1Discounted Sodium Cyanide (CAS: 143-33-9) for Mining - High Quality & Competitive Pricing
- 2China's New Regulations on Sodium Cyanide Exports and Guidance for International Buyers
- 3Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 4International Cyanide(Sodium cyanide) Management Code - Gold Mine Acceptance Standards
- 5China factory Sulfuric Acid 98%
- 6Anhydrous Oxalic acid 99.6% Industrial Grade
- 7Oxalic acid for mining 99.6%
- 1Sodium Cyanide 98% CAS 143-33-9 gold dressing agent Essential for Mining and Chemical Industries
- 2High Quality 99% Purity of Cyanuric chloride ISO 9001:2005 REACH Verified Producer
- 3Zinc chloride ZnCl2 for High Molecular Weight Polymers Initiator
- 4High Purity · Stable Performance · Higher Recovery — sodium cyanide for modern gold leaching
- 5High Quality Sodium Ferrocyanide / Sodium Hexacyanoferr
- 6Gold Ore Dressing Agent Safe Gold Extracting Agent Replace Sodium Cyanide
- 7Sodium Cyanide 98%+ CAS 143-33-9










Online message consultation
Add comment: